How to set up Google Search Console for your SEO strategy
Learn the simple steps on how to set up Google Search Console to start getting metrics on your SERPs and leverage information to accelerate growth.
Sometimes, it’s all about the low-hanging fruit.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of improving your website’s visibility on search engines and AI search tools. Several factors determine your website’s ranking on the search engine results pages (SERP). This includes site accessibility, page speed, optimized content, keywords, title tags, alt text––the list goes on.
On-page SEO is the low-hanging fruit of SEO. It’s the stuff that you have control over on Google, and can change up on your website at any time. Because you get to choose what content is on your pages, it’s even more important to put the right content on your pages.
One wrong move and you can deplete your rankings and risk penalization. One right move and you’re at the top of the SERP.
Here’s everything you need to know to nail your on-page SEO.
SEO helps maximize the results of your content from search engines, including improving your, SERP rankings, organic traffic, and organic conversions. On-page SEO edits means updating your pages for quick wins and overall improvements. This may include:
While you have the freedom to choose what’s on the page and what edits you make, on-page SEO requires a very specific recipe to see results. You need to be mindful and plan your strategy, or risk losing your rankings.
There are three main elements of SEO to consider when doing your edits: high-quality content, source code, and your website structure, as they all impact your site visibility, organic traffic, SERP rankings, and conversions.
Pro Tip: In addition to on-page SEO, you also need an off-page and SEO strategy to help your overall website look more attractive to search engines and perform how you want it to. Off-page SEO is a form of link building through strategies like PR opportunities and backlinks. On-page SEO focuses on things like site speed, sitemaps, crawling, indexing, rendering, engagement, user experience, and website architecture.
Find out what CEOs need to know about SEO here.
On-page SEO is key to improving your SERP rankings, and if done right, it tells Google and search engines about the content on your website, and more importantly, how you provide value to visitors and your customers.
When it comes to SERP rankings and increasing organic traffic, simply creating and publishing content on your website isn't enough—you must add value. This means, not only optimizing your content for search engines, but also for human experience if you want to increase your visibility.
Google is looking for the most relevant search result for a query, so their algorithms also look for other relevant content on the page. This content must add value and best answer the searcher’s query. For example, if your page is about cars and you don’t mention different makes, models, etc., Google will likely suggest more relevant web pages to the reader.
On-page SEO edits ensure your website content is optimized for humans (your customers) and search engine bots, so you can achieve the results you’re looking for.
When thinking about SEO and making tweaks to your content or website, be mindful of your execution. There’s a right way to do it and a wrong way to do it. Unethical, or black hat SEO, is all about cutting corners for immediate, short-term rankings. While white hat SEO involves creating high-quality content that adds value.
As mentioned above, Google is looking for pages that best answer a searcher’s query. So, if you’re taking a black hat or even a grey hat approach, you won’t get very far.
In fact, Google may penalize you in two ways. First, the spam team could identify a problem with your website and issue a manual action. Second, you could suffer an automated drop in rankings due to an update to Google's search algorithm. In both cases, you will need to find the root cause of the decline and resolve it.
Note: There may be a possibility that you’re receiving a Google penalty if your website traffic suddenly drops and you see a corresponding decline in rankings.
Google's Webmaster Guidelines states the following when it comes to the basic principles of SEO:
Avoid tricks intended to improve search engine rankings. A good rule of thumb is whether you'd feel comfortable explaining what you've done to a website that competes with you, or to a Google employee. Another useful test is to ask, "Does this help my users? Would I do this if search engines didn't exist?"
This is a good thing to keep in mind as you complete your on-page SEO strategy.
On-page SEO is called "on-page" because the tweaks and changes you make to optimize your website can be seen by visitors on your page (whereas off-page and technical SEO elements aren't always visible, but still make an impact).
Regardless, there are still technical elements you need to consider and do for your on-page SEO strategy, like crawling and indexing your website are crucial. First, search engines must crawl the internet for content, looking over the code/content for each URL they find. Next, this content is indexed, stored and organized. Once a page is in the index, it’s in the running to be displayed as a result to relevant queries.
One way to check your indexed pages is to use "site:yourdomain.com", an advanced search operator. Go to Google and type "site:yourdomain.com" into the search bar. This will return results Google has in its index for the site specified. You can also add additional identifiers and search for specific pages, keywords or topics using “inurl:”, “intitle:”, and “intext:”. See the full list of Google Search Operators here.
Once displayed, you can build an on-page SEO plan to improve your content. Every part of on-page SEO is completely up to you. That's why it's critical that you do it correctly and make the right decisions.
Before you go in to make your edits and build your strategy:
Now that you know everything to consider for on-page SEO, have conducted your content audit, and know your keyword rankings, there are 10 steps to effectively optimize and edit your page content for search.
Google ranks pages highly because it has determined they are the best answers to the searcher’s query. This means that your page has to provide value to searchers and be better than any other page Google has for it.
Not only that, but you also need to consider keyword density on your pages so you don’t stuff it with keywords and risk penalization. In fact, most SEO experts believe that an ideal keyword density is around 1-2%. This means the target keyword appears about one to two times per 100 words.
It’s also a good practice to use your main keyword once in the first 100-150 words of your article because Google puts more weight on terms that show up early in your page. It’s an old school on-page SEO tactic that still makes a difference.
In addition to structure, the content on your pages matter so you can increase your dwell time. In fact, KPIs to help you understand if your page is performing well may include time on page and bounce rate. And, if your content is too brief or specific, you can embed videos in order to reduce bounce rates and increase dwell time.
Note: If your average time on page is less than 60 seconds, your page’s content may not answer your searcher’s query.
Be sure that you’re also following a link building strategy.
Your title tag has more potential than you might realize. It’s what people see if you were to pop up on Google. Add keywords, keep them under 70 characters, and make sure your title tags add value to the reader and make them interested to learn more. This also includes optimizing your organic click through rate (CTR), which can drive more traffic to your site.
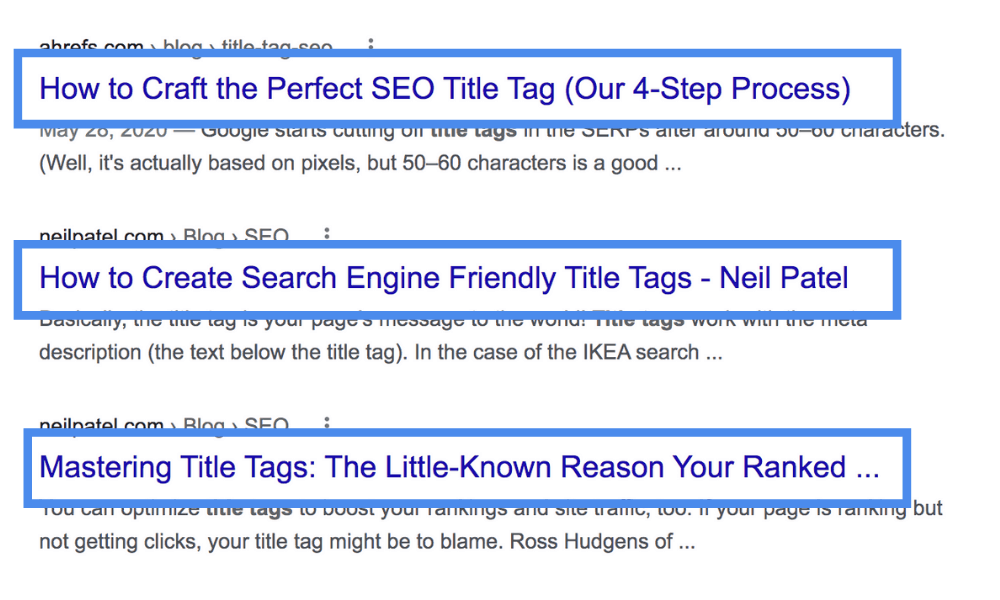
Meta descriptions are what show beneath your site's title tag on the SERPs. They encourage a user to click on your listing over someone else's for that query and also affect your organic CTR.
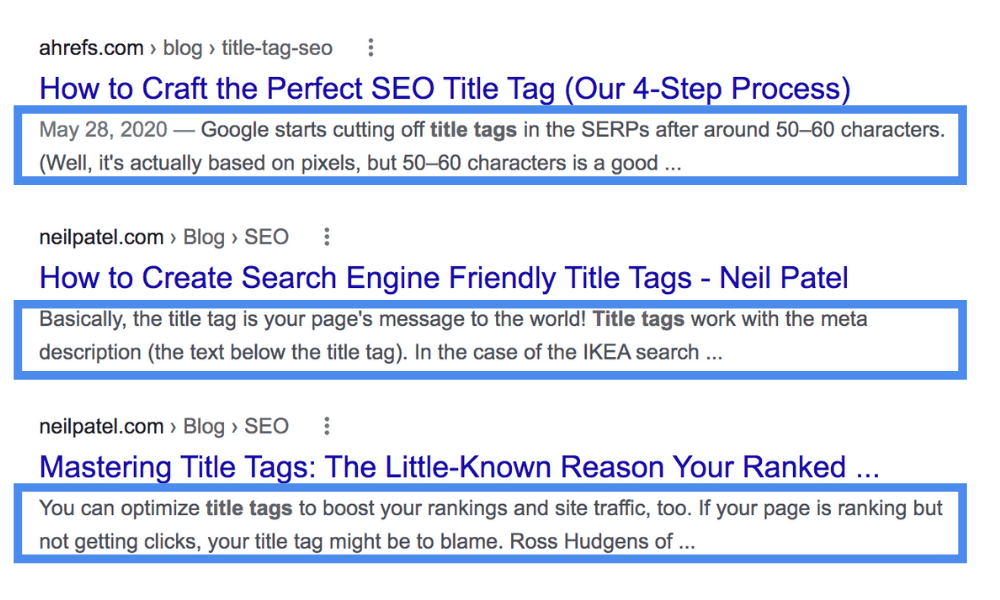
Note: If you don't have a meta description in place, Google will display part of your page's content. This could include navigation text and other elements that may not be as enticing, so it’s best practice to write a unique description. Make sure to avoid duplicates.
Don’t forget - structure matters. Your header tags provide structure and context for your article. Make sure the information in your post is well structured, and be sure to use the appropriate headers tags to display a consistent information hierarchy- H1, H2, H3, H4 etc. Your title should always be your H1, the main descriptive title of the page with primary keyword or phrase, followed by your H2 etc., with keyword variations. It’s best practice to only have one H1 on each of your pages to keep them specific about one topic.
Shorter URLs are best practice and make your pages more popular because they’re more readable, user-friendly and easier to share. The proper use of URLs can also help improve click-through rates when links are shared.
Standardize and shorten your URLs–use hyphens, not underscores, and make sure they’re relevant to the content on the page.

You should always pay attention to image optimization. This includes image optimizing the size and quality, but also properly naming images with a descriptive file naming convention.
Alt image text helps screen-reading tools describe images to visually impaired readers and allows search engine bots to better crawl and rank your website. It’s also another good way to get some keywords into your post, however, you should ensure that the main images on each page of your site use alt tags to properly describe the content. Use variants of your focus keyword across alt images, but don’t keyword stuff the same term over and over. This will negatively impact your SEO and can even lead Google to ‘blacklist’ your content.
Load time matters. Always. In fact, pages that load within two seconds have an average bounce rate of 9%, while pages that load in five seconds see their bounce rates skyrocket to 38%. What’s the point of optimizing your content if users are just going to bounce while they wait for it to load? Google's page speed insights tool will provide more information on the page speed score of your website and how to improve this.
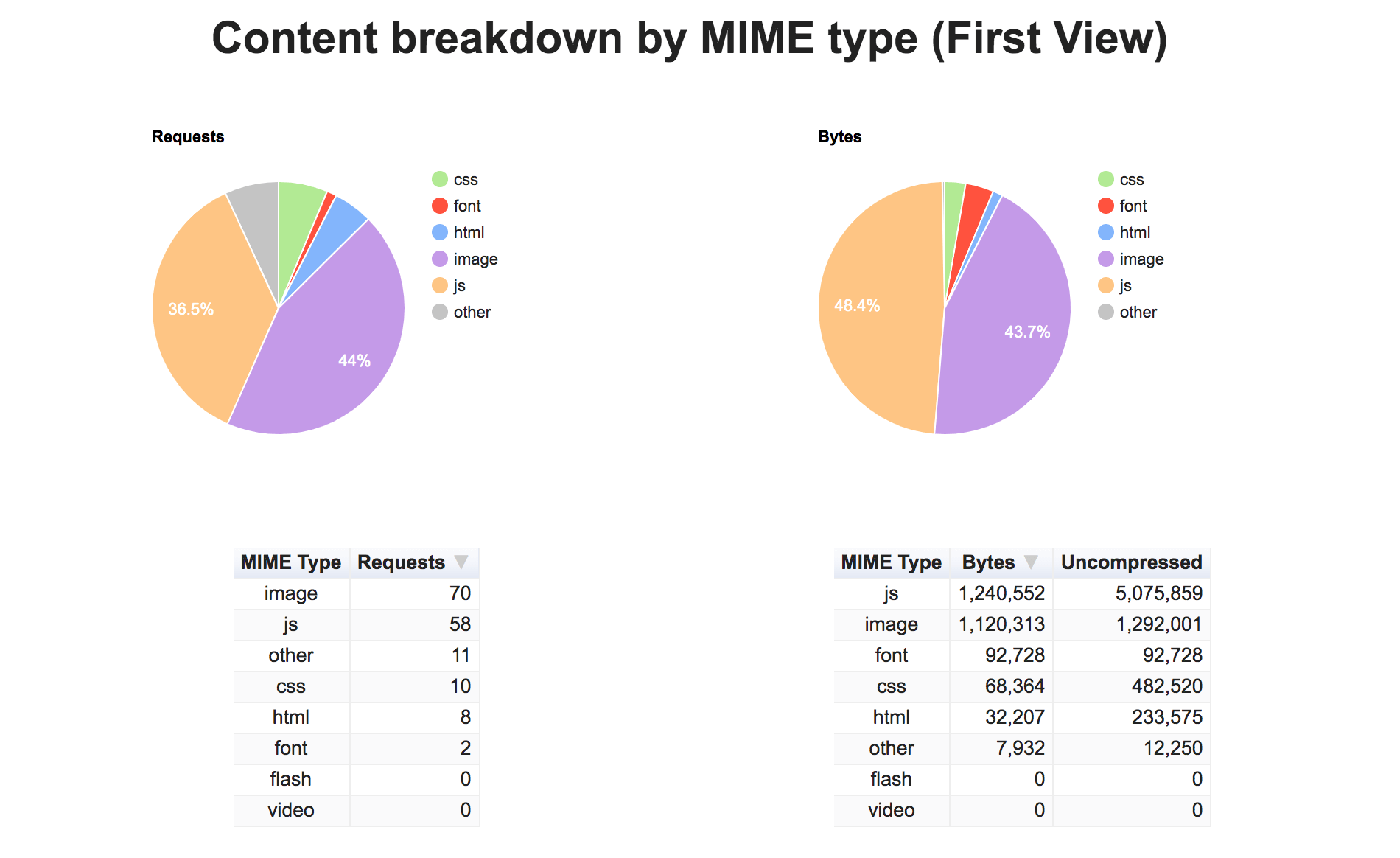
If you want a breakdown, WebPageTest is also a good tool to use. As you can see below, slower page speeds for this site are largely attributed to Javascript and image file size. In this case, the focus should be on compressing images and optimizing code. This means reducing the size of Javascript, such as removing spaces, commas, formatting, and other unnecessary or unused characters.
Always always always be sure your website is mobile-friendly. More than half (60%) of all search volume results from smartphones, according to Google mobile search stats. In fact, 53% of mobile site visits are abandoned if the page takes more than three seconds to load. Not only is it important to have a responsive page, but a good mobile speed score for your website (50-89 out of 100 is average).
In addition to looking at responsive design elements, Google also looks at the performance of your mobile page as a ranking factor. You can also leverage accelerated mobile pages (AMP) for fast load times for mobile users. AMP pages are essentially stripped down HTML copies of existing webpage content that offer much faster load times than standard HTML5 documents.
When you link to other pages on your website, you ensure that search engine crawlers can find all your website’s pages. You also pass link equity (ranking power) to other pages on your site, which also helps visitors navigate your site. This especially comes into play if you are focusing on a topic cluster strategy for your content.
Internal links are arguably one of the most neglected link building tactics in SEO marketing. Spending time improving your site's internal linking strategy almost always drives noticeable gains quite quickly.
Some marketers see really quick wins from adding even one or two internal links from authoritative pages elsewhere on your site.
Adding Schema markup to your HTML improves the way your page is seen in SERPs by enhancing the rich snippets that are displayed beneath the page title. Schema is the result of collaboration between Google, Bing, Yandex, and Yahoo! to help you provide the information their search engines need to understand your content so they can display the best search results possible.
For example, in the example below, the first search result contains a rich snippet star review rating, which can be added using Schema. The second and third examples display either the meta description or other information chosen by Google.
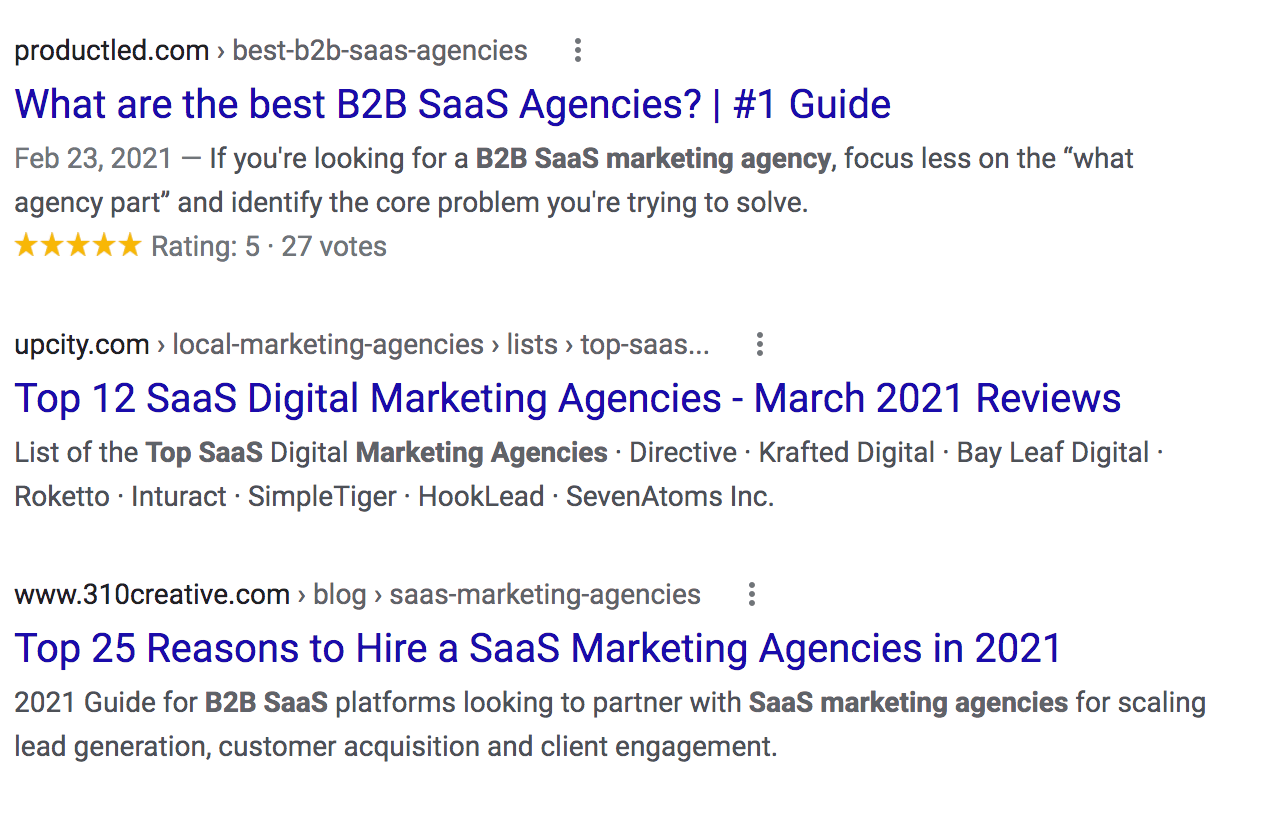
You can add your own Schema using Google's Structured Data Markup Helper.
All of this adds up to the holistic user experience on your page. This is a set of signals that measure how users perceive the experience of interacting with a page beyond its pure information value. Signals include visualizations, page speed, mobile-friendliness, visibility, and usability.
User experience is also a good way to improve dwell time on your page. This can includes anything that makes your content easier to read, such as:
On-page SEO isn’t limited to all of the above, but these are the general areas you want to start when thinking about optimizing your content for search engines.
Don’t forget, you’re not only optimizing for search engines. You’re also optimizing for people–your readers.
On-page SEO is ongoing. This means you should also monitor for new opportunities to improve. To start, crawl and index your website and evaluate its health and current content in order to make the right decisions for optimization.
Below are some helpful tools to use as you start to build and execute your SEO strategy and monitor performance for future optimizations.
*Don’t forget to use an analytics tool like Google Analytics or Hubspot to measure the performance of your pages and content beyond the keyword rankings and technical elements.
Remember, Google ranks pages highly when it determines they are the best answers to the specific search query. This means your page needs to provide value to searchers and be better than any other content ranking for that topic.
On-page SEO not only ensures high-quality content and better rankings, but it also requires continuous monitoring to improve. Be sure to track your metrics on a dashboard. It’s also important to keep in mind that rankings fluctuate each time content is indexed. This means what has dropped 2 positions today, could climb 5 positions next week. Make smart decisions and keep a close eye on changes.
The best way to keep your website ranking well is to follow Google's Webmaster Guidelines.
Fadi co-founded Kalungi in 2018 with Stijn Hendrikse. He has over 20 years of experience in marketing and building businesses. He is a certified HubSpot Champion User.
Learn the simple steps on how to set up Google Search Console to start getting metrics on your SERPs and leverage information to accelerate growth.
Six proven writing prompt examples you can send to your next interview candidates.
If you can get your customers to USE, LIKE and SHARE you're on your way to great churn reduction. These users are called Engaged Advocates.
Be the first to know about new B2B SaaS Marketing insights to build or refine your marketing function with the tools and knowledge of today’s industry.