The SaaS Strategy Gap: Why You’re Not Ready for Growth (Even If You Think You Are)
Hidden SaaS strategy gaps can destroy your growth potential. Discover how to fix them and grow better!

Growth is the lifeblood of any SaaS company, but it doesn’t happen by accident.
Behind every successful SaaS business is a well-thought-out strategy, one that balances ambition with focus. And if you’re looking for a tool to guide that strategy, the Growth Matrix –also known as Ansoff Matrix– might just be your new best friend.
This simple yet powerful framework helps SaaS founders and executives prioritize growth opportunities, assess risks, and align their teams. Whether you’re doubling down on your current market, expanding into new ones, or innovating with new products, the Growth Matrix gives you a clear path forward.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to harness the power of the Growth Matrix to supercharge your go-to-market strategy and achieve sustainable, scalable growth.
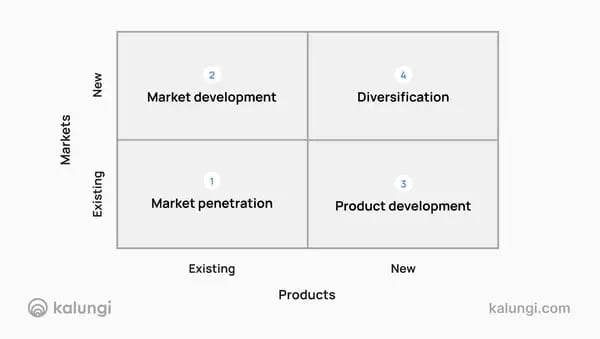
The Growth Matrix is a strategic planning framework designed to help businesses identify and evaluate growth opportunities.
Created by Igor Ansoff in 1957, it divides growth strategies into four categories: Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development, and Diversification.
Each strategy represents a different level of risk and requires a unique approach to execution.
For SaaS companies, this matrix is a practical framework for deciding where to invest resources, how to tackle market challenges, and what risks are worth taking.
The Growth Matrix is a decision-making tool for prioritizing growth opportunities. For SaaS companies, it helps answer critical questions like:
It’s especially valuable for aligning your leadership team around a shared understanding of where growth will come from, and for avoiding the trap of chasing too many directions at once.
This is the “safe zone” of the matrix.
Market penetration is about increasing your share of an existing market with your current product lineup.
For SaaS companies, this could mean upselling premium features to existing users, reducing churn, or ramping up marketing efforts to capture a larger slice of your existing customer base.
Some strategies for SaaS market penetration are:
Market penetration works best when your product already has traction in its current market, but there’s still untapped potential.
👉 Listen to our podcast episode "Get more market penetration with Ansoff’s Matrix" here.
Market development means taking your existing product and introducing it to new customer segments, industries, or geographies.
For SaaS, this might mean entering new verticals, targeting enterprise customers after starting with SMBs, or expanding to international markets.
Some strategies for SaaS market development are:
While market development can open up significant growth opportunities, it also requires deep market research and operational adjustments.
👉 Listen to our podcast episode "Expand your market with Ansoff’s Matrix" here.
This quadrant is all about innovation.
You’re focusing on delivering new value to your current market, whether that’s through adding features, creating complementary tools, or launching entirely new products.
Some strategies for SaaS product development are:
Product development is ideal for SaaS companies with a loyal customer base that’s asking for more, or when you spot gaps in your product offering that could drive higher revenue.
👉 Listen to our podcast episode "Pivoting and product development with Ansoff's Matrix" here.
Diversification is the boldest strategy because you will be creating new products for entirely new markets.
While high-risk, it can be a game-changer if executed well. For SaaS, this might mean launching a completely new product that serves a different type of customer or entering an adjacent market.
Some strategies for SaaS diversification are:
Diversification should be approached carefully and typically works best when you have the resources to manage the inherent risks.
SaaS founders and executives often face a common challenge: too many growth opportunities, too little time.
The Growth Matrix helps you cut through the noise and focus on initiatives that align with your company’s stage, market conditions, and revenue goals.
The Growth Matrix is critical for your SaaS GTM strategy because it:
In the SaaS industry, having a structured approach like the Growth Matrix is what turns reactive decision-making into proactive strategy.
Now that you see why the Growth Matrix is a game-changer for SaaS growth, let’s dive into how you can bring it to life. The real magic happens during the Growth Matrix exercise.
At Kalungi, the Growth Matrix exercise is exercise 1 (of 7) in our go-to-market workshop deep-dive series, a hands-on, collaborative process that transforms big-picture strategy into clear, actionable priorities for your team.
This exercise forms the basis for your entire go-to-market strategy.
The Growth Matrix exercise helps your team align on and prioritize your company’s most important initiatives, then gives you a framework to decide how to pursue each one. It should be an essential component of your SaaS go-to-market workshop.
The final result tells you which of the four key growth strategies you should pursue over the next 6–12 months—and how much effort you should put into each one.
The product market Growth Matrix tells you what to build your OKRs around, provides a baseline for creating funnel projections, shows you where to focus your team’s time, and helps you create guardrails for saying ‘yes’ (and ‘no’) to new initiatives that support your company's ultimate goals.
After running this exercise (and applying some strategic thinking to the results), you should be able to say something like this:
“Our go-to-market strategy consists of two main efforts:
1) entering new markets with our current product and 2) taking more market share with our current products.20% of our effort will be dedicated to entering new markets through [Growth lever 2], [Growth lever 2], and [Growth lever 3]"
The other 80% of our effort will be dedicated to taking more market share through [Growth lever 4], [Growth lever 5], and [Growth lever 6]."
Convincing a large group of your highest-impact leaders to spend a few hours in a room together for an exercise can be difficult. But—speaking from experience—it’s well worth the effort.
Skipping over this exercise runs the risk of your leadership team prioritizing conflicting efforts because they have their own interpretation of where the company’s growth should come from—and the role their department should play in getting there.
If you don’t have a clear big picture, you have an environment of unfocused work with your team doing random acts of marketing to hit short-term growth goals and forgetting the bigger picture.
A thoroughly completed Growth Matrix gives your team a north star to compare every effort against. For each new project or initiative, you can ask: “Does this fit into our overall growth plan?” If the answer is “no,” it's ok to deprioritize it.
.webp?width=670&height=274&name=Chart-which-growth-stage-should-you-try-ansoffs-growth-matrix-exercise-at-1%20(1).webp) Within the T2D3 growth stage framework, the Growth Matrix is most helpful once you've found some degree of product-market fit.
Within the T2D3 growth stage framework, the Growth Matrix is most helpful once you've found some degree of product-market fit.
If customers aren’t paying to use your product yet (i.e., you're still in the MVP growth stage), it’s harder to get meaningful results from the Growth Matrix exercise. In the MVP stage, most of your results will land in the “product development” quadrant (bottom right).
This only reinforces the goal we know you should be focused on at the MVP stage: building features that help you find your first paying customers. Of course, this isn't always the case—but a word of caution for very early-stage companies considering using this exercise.
The purpose of running an Growth Matrix exercise is to create a structured, collaborative process to align your leadership team on the most impactful growth priorities.
Kalungi’s step-by-step guide will help you facilitate a session that transforms high-level strategy into actionable plans your SaaS business can execute with confidence.
Start by explaining the philosophy of the matrix to the workshop attendees. We often use the example of a winemaker to explain the premise of the Growth Matrix. Here's a snippet you can modify to get started
Imagine your company makes wine. You need to grow revenue by $1,000,000 dollars in the next 12 months. To do this, you could pursue four different strategies. Each strategy fits into a different quadrant on the matrix:
Within each strategy, there are different growth levers (tactics) you can pull. For example: In the “Take more market share” list item (bullet #1), you could do one (or all) of the following:
If you pretend our company is the winemaker, our time together aims to uncover all of the potential ways we can sell more of our wine (software). Once we have all of our ideas out on the table, we’ll decide which have the biggest impact potential and come up with clear priorities for our team to work on in the coming year.
It helps to show a visual of the matrix while you explain the winemaker example above. I find this helps workshop attendees connect the examples with each quadrant.
1. Launch a Miro board (or equivalent whiteboarding tool) with four quadrants and X and Y labels from the diagram in the section above. If you’re facilitating the exercise in person, draw a 2x2 grid on a whiteboard or paper easel and grab some colorful sticky notes.
Below is the Miro template we built for this exercise. To get this template, sign-up for early access to the Kalungi App..webp?width=654&height=263&name=Screenshot-of-Kalungis-Ansoffs-growth-matrix-exercise-Miro-template-min-1%20(1).webp)
2. Before starting, define your company’s growth target with the group. Usually, the CEO can provide this number. This will frame the conversation and get your participants to think about how each tactic will tie back to revenue. Your growth target should have a dollar and time value. For example, it could be: “+$1 Million Annual Recurring Revenue in 12 months.” Write this number in the center of your matrix and circle it. Explain to your group that the rest of the exercise should be completed with this growth target in mind.
3. Give participants 5 minutes to create a small collection of 3–5 sticky notes. Each sticky note should include the following participant prompts
- Describe the growth lever
- Estimate the number of new customers this tactic will generate in the period you defined in your growth target
- Estimate the annual contract value (ACV) for each new customer
- Estimate the relative difficulty of implementing this growth lever within the company
Here are some examples of what your participant’s stickies might look like. Note: it’s ok if not all stickies have values for “New customers” or “ACV.” Some tactics are hard to tie directly to revenue. These will be discussed with the group later. Your goal right now is to collect ideas.
4. Ask everyone to place their sticky notes in the best-suited quadrant of the Growth Matrix.
Go through the notes together. Pick out a few strong standouts. Ask the creators to explain the tactic and the rationale behind it.
5. Adjust sticky placement within the proper quadrants, if necessary—but don’t worry about perfection. You’ll be able to reorganize these and add additional details after the workshop.
6. Ask each member to present 2–3 of their stickies to the group. As the facilitator, I recommend taking additional notes when each sticky is presented. Participants often write shorthand or abbreviate their ideas on the sticky note—but there's usually more complexity to the idea when it's described out loud. Some questions you can ask to facilitate this discussion:
- Why did you choose to contribute this growth lever?
- Can you explain the logic behind the opportunity size/new customer/ACV/effort value you wrote.
7. During step 6, it’s ok to challenge group members on the placement of stickies. Showing them the proper quadrant for their sticky is a good conversation starter and sometimes uncovers hidden meaning/intent in the sticky when the creator explains it.
8. If you end up with multiple overlapping stickies, collect them into thematic groups on the whiteboard with other similar stickies.
9. Collect feedback from the group on which growth levers they think are best to invest in by facilitating a vote. Have each member vote on the top 3–5 initiatives they believe will be most impactful across the 4 quadrants. You can use Miro's voting mechanic or, if you're in-person, have members place colored dots on the stickies they like best.
10. Discuss the results with the group. You should be able to create a rough stack rank of the initiatives after this discussion.
Here are two examples of what your growth matrix board might look like after you run Step 2. Note: these screenshots were from growth matrix exercises run in Stormboard.
%201%20(1).webp?width=670&height=407&name=Ansoff%20Growth%20Matrix%20-%20completed%20example%20in%20a%20go%20to%20market%20workshop%20(1)%201%20(1).webp)
.webp?width=670&height=365&name=Ansoff-Growth-Matrix-completed-example-in-a-go-to-market-workshop-_2_-1%20(1).webp)
If you need examples to generate ideas for your workshop members, share this list of growth lever examples with them.
After the exercise (and with some space to breathe & go deep), compile the results of your Growth Matrix in a growth priority spreadsheet like the one pictured below.
This step lets you add detail and nuance to each lever that many of the workshop stickies won't have—since most workshop participants use short-hand to fit their ideas onto a single card.
Here, you can parse out details from each sticky into different columns and use sorting mechanisms to look for patterns. For example, you might look first for growth levers with a low-cost rating and high potential for recurring revenue opportunities.
It’s important to note that not all of your growth levers will contribute to recurring revenue growth. Some might be one-time revenue generators that you may decide to ignore for now because it doesn’t support a growth target that focuses on recurring revenue.
.webp?width=670&height=364&name=Kalungi%20-%20B2B%20SaaS%20growth%20priority%20spreadsheet%20example%20-%20T2D3%201%20(1).webp)
Use your growth priority spreadsheet to select the growth levers you want to pursue based on their estimated ARR impact, priority from the group, and feasibility in the short to medium term.
Group the most impactful levers into overarching themes and present the collection to your leadership team. This exercise isn't complete until your department leaders arrive at a collective agreement that they will use this mix of growth priorities to inform their goals and decisions over the coming year.
Once you've received confirmation on the plan, formalize the growth priorities on a single slide in your go-to-market summary deck. I find the format below helpful for summarizing the key pillars without too much painstaking detail. This slide should strike a balance between strategic storytelling and tactical specificity so it can be useful for everyone from your board to your team.
Below is an example of what your output slide could look like from this exercise.
%202%20(1).webp?width=670&height=440&name=Complete%20example%20of%20Ansoffs%20growth%20matrix%20in%20a%20B2B%20SaaS%20go-to-market%20strategy%20-%20Kalungi%20(1)%202%20(1).webp)
Now that you've set your company's growth priorities, you can start building your objectives and key results around them.
By using the output of your Ansoff Matrix as the foundation for your OKRs , you're nearly guaranteeing that your team is creating key results that support your growth principles and moving in the same direction.
At Kalungi, we specialize in helping SaaS companies navigate growth challenges by providing proven frameworks like the Growth Matrix as part of our go-to-market workshop series.
Whether you're looking to enter new markets, optimize your product strategy, or prioritize high-ROI growth levers, we’re here to guide you every step of the way.
Ready to get started? Book a free discovery call with our team to learn how Kalungi can help you build and execute a winning GTM strategy tailored to your SaaS business.
An in-depth guide on what OKRs are, why they’re important for B2B SaaS marketing teams, and how to create them.
B2B SaaS marketing OKR examples and a template to help you balance driving demand, sustainable growth, and good ROI.
Mike was Kalungi's Head of Product and Marketing. He is also the co-author of T2D3 with Stijn Hendrikse.
Hidden SaaS strategy gaps can destroy your growth potential. Discover how to fix them and grow better!
Learn how to use the Ansoff Matrix to guide your SaaS GTM strategy. Discover insights to prioritize growth, align your team, and scale sustainably.
Find the CRM that provides the interconnectivity you need to maximize your customer journey and unlock your B2B SaaS growth.
Be the first to know about new B2B SaaS Marketing insights to build or refine your marketing function with the tools and knowledge of today’s industry.