Redirects are a valuable tool in keeping site authority on search engines and general site health at a top-notch level. Let’s take a look at what redirects are, how they work, and what to do with them.
What are URL redirects and why do we use them?
Redirecting is when one URL is pointed to a new destination. We use them when content is either outdated or has been unpublished and archived, giving users a place to go instead of landing on a 404 page. There are two types of redirects we mainly see:
301: A permanent redirect that signals search engines that the new content will officially live in this new location.
302: A temporary redirect that should only be used if you plan to remove the content/URL later in place of something new and updated. An example of this would be if you wanted to send someone to a new page for a short or limited amount of time. You set up the 302 redirects and tell google that this page will only be up for a short amount of time.
In most cases, we will only see the 301 types of redirect used since most changes will be considered permanent and is a good way to keep moving forward through any roadmap you might have without needing to go back and change things.
Is it easy?
Many current CMS providers make this an easy automated process while some others will make you do a little more work. All you need is the current URL, the URL you want it to go to, and whether you want it to be permanent or temporary. Systems like Hubspot will make this easy on you by automatically creating one when any URL is changed in the page settings. You can also head into the Domain&URLs area and change/add any of this manually. Here’s a quick step-by-step guide on how to do that.
Step 1: Go to HubSpot settings, on the left-hand sidebar menu navigate to Website ➜ Domains & URLs then proceed to URL Redirects in this new section.
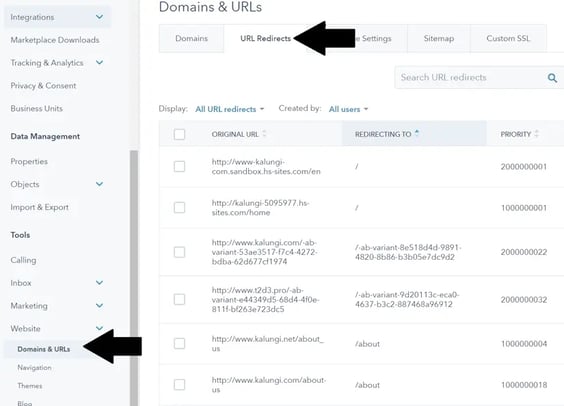
Step 2: Click on Add URL redirect to create a new entry or go to actions and edit an existing redirect to make updates.
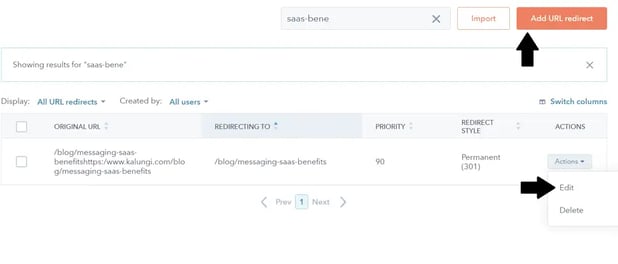
Step 3: Make sure the standard redirect is selected. Then, enter the original URL in the first box and the new destination in the second box.
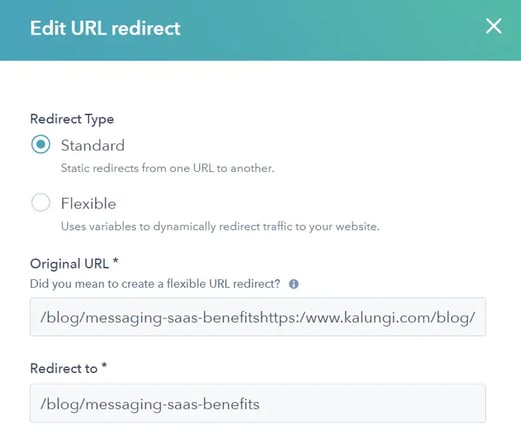
Step 4: Under more options, choose the priority to give to the URL, its redirect style, and how the redirect can be read.
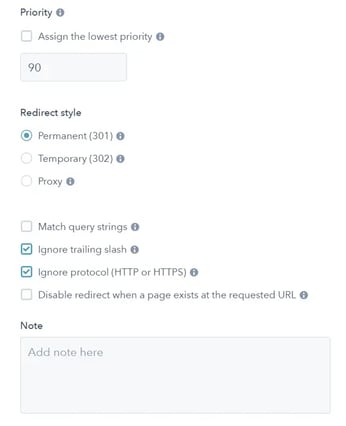
Step 5: Update your URL changes!
Other providers with cheaper, more affordable options such as Squarespace tend to have a more manual system in place. For every URL change, you need to go to the URL section Squarespace and enter a string that tells them what to do. Something along the lines of {url1} -> {url2} {redirect type}. Below is an example of one page being redirected using this format.
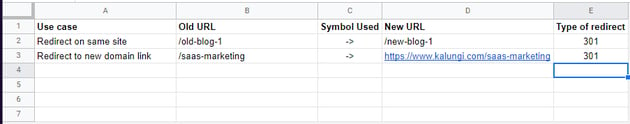
How long should I keep my redirects?
If you’ve had your website for a while, there's a good chance that you’ve changed your URLs at least a few times throughout its lifetime while optimizing or creating new content. It can take a couple of days to a few weeks for some pages to be indexed so be patient and monitor the status of the new pages weekly if they are having problems.
If Google finds that any URL is no longer relevant, it will eventually remove it from its ecosystem, providing no more information on its Google Search Console tool. With how Google adds and removes pages, you might be wondering if you should always keep any URL you create or if someone from 5 years ago still has this old link and needs to access it. The best way to approach this is by forwarding the entire old domain to the new homepage.
Here’s a checklist to look at for removing any redirects:
- The new content has been up for an extended period of time
- Google has had the opportunity to remove the old URL from its database
- You don’t think it generates any traffic
You are free to delete the redirect if it passes all of these and you are comfortable doing so.
Does my redirect library need maintenance?
Having too many redirects can create a long redirect chain which will start to take up resources and just start to turn into a mess. It is advised to have a redirect chain no longer than 4 URLs from the original source. A good way to clean up this problem is by taking each unique URL and pointing it to the end destination.
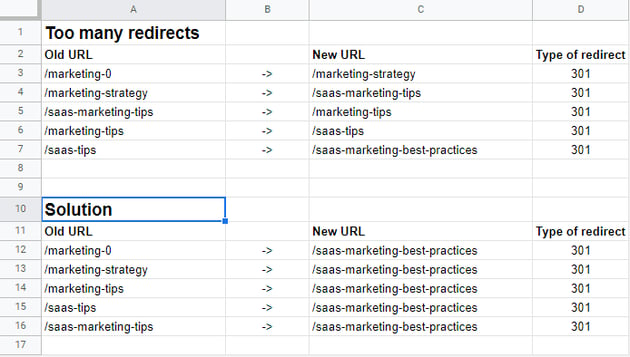
Hopefully, these tips will help as you work through making sure each piece of content you publish and its authority has a place to go after it's been updated or removed. This will help you with your rankings and prevent visitors from scratching their heads wondering where the post they were looking for is. Check out this post on how to set up Google Search Console works so that you can have more control over your SEO health!